Table of Contents
CrEDIBLE thematic working days, October 2-4, 2013
Due to the increasing on-line availability of various biomedical data sources, the ability to federate heterogeneous and distributed data sources becomes critical to support multi-centric studies and translational research in medicine. The CrEDIBLE project organises 3 thematic working days in October 2-4 in Sophia Antipolis (near to Nice, France) where experts are invited to present their latest work and discuss their approaches. The aim is to gather scientists from all disciplines involved in the set up of distributed and heterogeneous medical data sharing systems (medical data representation, data mediation, data stores federation, data semantics, workflows, … towards biomedical data integration), to provide an overview of this broad and complex area, to assess the state-of-the-art methods and technologies addressing it, and to discuss the open scientific questions it raises.
The methods for biomedical data distribution considered in the context of CrEDIBLE are:
- Federation: the (virtual) fusion of geographically spread data stores which should appear to end users as a unique and coherent data source.
- Mediation: the semantic alignment of heterogeneous data sources, which were often designed independently from each other.
- Querying: the description of distributed data sets, defined through data retrieval queries that apply on the whole federated system.
- Data flow: the use and the enrichment of the federated data stores through the use of data processing pipelines.
A previous issue of this workshop was organised on October 2012.
Working days organisation
The idea of this workshop it to have groups of ~30 minutes presentations within a given theme/session followed by a time slot for a panel discussion to share the presenters experience on selected scientific questions and challenges. Talks should keep a balance between introducing the field (appropriate for a broad audience of scientists involved in all the areas covered by CrEDIBLE) and technical details (appropriate for expert scientists).
Thematic sessions
Session 1: Data repositories for secondary use of clinical and research data
Session goal: To report on concrete experience in developing systems gathering or indexing data to be shared and reused in research projects. User requirements, current technology limitations and future expectations.
Scientific questions:
- Data indexing: how to meet the expectations of researchers in terms of precision of the vocabulary
- Data provenance: what do we need actually: detailed models of provenance ? or more “distilled” information ?
- Access control: how to accomodate multiple access policies specified by contributing entities ? is it manageable in practice ? should it be applied to datasets only (e.g. images, signals) or to metadata as well ?
- Data federation: what level of data federation is required? What are the data sources to federate? What are the data models in use?
Session 2: Biomedical ontologies
Session goal: To discuss ontologies modeling observations and measurements data (designed to facilitate the sharing and reuse of scientific data)
Scientific questions:
- modelling related entities (observed entity, measured quality, measurement results, units of measurements) and relationships
- relation with foundational ontology (ies) such as DOLCE, DOLCE-CORE and BFO ? compatibility ?
- relation to existing ontologies of qualities
- how to model complex observation data such as images ? notion of field ?
- how to model time varying phenomena ?
Session 3: Data mediation
Context: heterogeneous data stores, within the same or related domains (e.g. biology, medical images, clinical records…), sensitive.
Scientific questions:
- Reference model. Taxonomies or ontologies can be used as reference model. Is this the most appropriate reference model? What are the target models of the methods presented.
- Query language. SPARQL can be used as query language to access data in heterogeneous databases. Is it the most appropriate query language? What are the query language applicable to the methods presented.
- How to mediate various data sources (Pros and cons of each approach. Use cases. Are there hybrid approaches?):
- statically (ETL): transform data source periodically (e.g. into RDF stores).
- dynamically: query on-the-fly.
- How to ensure access control in an heterogeneous deployment
- at coarse-grain (each data repository)
- at fine-grain (each entity within a data repository)
Session 4: Data federation
Context: non-partitioned data stores, no prior knowledge on stores content, common RDF representation, common reference ontology.
Scientific questions:
- Query language. Is SPARQL (v1.1) the most appropriate language? What is the trade-off between expressiveness and performance?
- Performance. What is the performance impact? Gain of parallel execution of queries vs network overhead?
- Especially when deploying over a WAN?
- Scalability. How scalable are the different methods proposed? To what scale have they been tested?
- Reliability. What is the impact of low reliability? Can queries be partially processed in case of communication failures with some data stores? Can end-users be notified on the kind of potentially missing information?
Session 5: Graphs and reasoning
Scientific questions:
- How to process large RDF graphs? Storage in databases, scalability of graph processing algorithms, graphs indexing.
- How can semantics described in ontologies be used to interpret RDF data? While the Web of data focusses on large data sets processing, the semantic Web involves costly reasoning processes. There is a trade-off to be found between the amount of data to process and the reasoning capabilities of the system.
- Other scalability opportunities when addressing data querying: top-k query answer algorithms, probabilistic algorithms?
- How to visualise large data graphs?
Agenda
Wednesday, October the 2nd, 2013
Welcome and introduction
- 14:00, Johan Montagnat (CNRS, France): Workshop introduction
Session 1: Data repositories for secondary use of clinical and research data
from 14:30 to 18:15
- 14:30, Marc Cuggia (U. Rennes 1, France): Secondary use of Clinical Data for Medical Research
- 15:00, Maryann Martone (UCSD, USA): Experience with the development and operation of the Neuroscience Information Framework (NIF) portal
- 15:30, Serena Villata (INRIA, FR): Applying open data provenance and licensing to biomedical data
- 16:00, coffee break
- 16:15, Khalid Belhajjame (U. Manchester, UK): Research Objects: Preserving Scientific Workflows and Their Provenance
- 16:45, Charles Marion (Kitware): Visualization and analysis of medical data through the Internet
- 17:15, Panel discussion. Moderators: Bernard Gibaud, Alban Gaignard
19:30, Diner at Hotel Omega
Thursday, October the 3rd, 2013
Session 2: Biomedical ontologies
from 9:00 to 12:45
- 9:00, Bernard Gibaud (INSERM, France) and Gilles Kassel (U. Picardie, France): Observation data semantics: an ontological approach
- 9:30, Claudio Masolo (LOA, ISTC-CNR, Trento, Italy): Quality-spaces: problematic aspects
- 10:00, Werner Kuhn (U. Münster): Ontology of observations in space and time
- 10:30, coffee break
- 10:45, Maryann Martone (UCSD, USA): Experience of indexing brain research related measurements with NIFSTD
- (cancelled) Georgio Gkoutos (U. Cambridge): The ontology of Units of measurements and their relations to qualities
- 11:15, Panel discussion. Moderators: Bernard Gibaud, Gilles Kassel
Session 3: Data mediation
from 14:00 to 16:00
- 14:00, Nuno Lopes (National University of Ireland Galway), XML data mediation using XSPARQL
- 14:30, Jérôme Euzenat (INRIA, France), Data mediation in SPARQL from alignments
- 15:00, Michel Vincent (Logilab, France), BRAINOMICS: A management system for exploring and merging heterogeneous brain mapping data based on CubicWeb
- 15:30, Panel discussion. Moderators: Franck Michel, Johan Montagnat
Session 4: Data federation
from 16:15 to 18:45
- 16:15, Andreas Schwarte (fluid Operations AG, Germany), FedX: A framework for efficiently evaluating SPARQL queries in a federated environment
- 16:45, Maria-Esther Vidal (U. Simón Bolívar, Caracas, Venezuela), On the Efficiency and Effectiveness of Federated Semantic Data Management - ANAPSID An Adaptive Approach
- 17:15, Pascal Molli (U. Nantes, France), SemLav: Local-As-View mediation for SPARQL Queries
- 17:45, François Paulus (SemSoft, France), Data federation tools at SemSoft
- 18:15, Panel discussion. Moderators: Johan Montagnat, Olivier Corby, Alban Gaignard
Friday, October the 4th, 2013
Session 5: Graphs and reasoning
from 9:00 to 12:00
- 9:00, Jacopo Urbani (Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam), Forward versus Backward: Two approaches for web-scale reasoning
- 9:30, Marie-Laure Mugnier (LIRMM, Montpellier, France), Ontology-based Query Answering with Existential Rules
- 10:00, Olivier Curé (Université Marne La Vallée, France), RDF triple stores and indexation
- 10:30, Panel discussion. Moderators: Catherine Faron-Zucker, Olivier Corby
- 11:15, coffee break
Workshop conclusions
- 11:30, Johan Montagnat (CNRS, France)
Venue
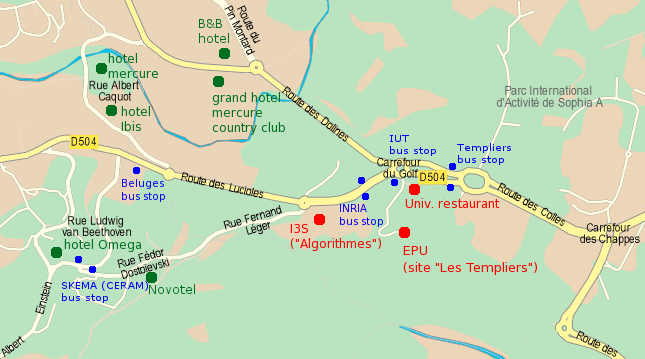
The workshop will be held in the conference room, located at the ground floor of the I3S laboratory, in Sophia Antipolis, France. The I3S laboratory address is: Building “Algorithms B”, 2000 route des Lucioles, BP 121, 06903 Sophia Antipolis Cedex, FRANCE
Where is it ?
- GPS coordinates:
- 43°36'56“ N
- 07°04'01” E
- See number [1] on the map below
How to go there ?
- By plane: "Nice Cote d'Azur" airport (NCE). There are two terminals (T1 and T2) with a free and frequent shuttle bus circling between the terminals.
- Taxi are available from both terminals. A taxi from the airport costs approximately 65 euros.
- During week days, from the airport T1 TAM bus number 230 (Sophia Express bus) is direct to Sophia Antipolis through the motorway (stop at the “INRIA” bus stop shown on the map). See the schedule.
- On saturdays, Sundays and Holidays you need to take metropolitan TAM bus number 200 (towards Cannes) and stop at the Antibes train station bridge (“passerelle SNCF” bus stop) before connecting to one of the buses from Antibes to Sophia Antipolis (see below). The buses time tables are sparse on Sundays and Holidays.
- The taxi or bus 230 ride is approximately 20 minutes out of rush hours.
- By train: “Antibes” train station. From the train station there are 3 options:
- Bus Envibus line number 11 is direct from Antibes train station (“SNCF” bus stop) to EPU building (“IUT” bus stop).
- Bus Envibus line number 1 runs from the train station bridge (“passerelle SNCF” bus stop) to Sophia Antipolis (“IUT bus stop”). Be aware that there are 2 buses number 1 line ends: “Lycée Léonard de Vinci” (these ones stops before reaching Sophia Antipolis) and “Gare Routière de Valbonne - Sophia Antipolis” (take one of these).
- Bus Envibus line number 9 runs from bus stop “Vautrin bas” (in the vicinity of the Antibes train station bridge, short walk on your left after crossing the bridge) to the “Belugues” bus stop in Sophia Antipolis (see map). Be aware that there are 2 buses number 9 line ends: “Lycée Léonard de Vinci” (these ones stops before reaching Sophia Antipolis) and “Gare Routière de Valbonne - Sophia Antipolis” (take one of these).
- By car: A8 highway. Exit at “Antibes - Sophia Antipolis” then follow Sophia Antipolis and reach “carrefour des Chappes” round-about on the map below.
- The I3S building is number “[1]” on the map below, which also shows the closest bus stops.
Also see the interactive map.
Nearby hotels
A list of nearby hotels (all within 10 minutes walking distance) is located on this map:
- B&B'hotel:
http://www.hotel-bb.com/hotel_info?hotelId=4532
- Hotel Ibis, 2 stars:
http://www.ibishotel.com/gb/hotel-0711-ibis-antibes-sophia-antipolis/index.shtml
- Hotel Mercure, 3 stars:
http://www.accorhotels.com/gb/hotel-1122-mercure-antibes-sophia-antipolis/index.shtml
- Hotel Omega, 3 stars:
http://www.hotelomega.com/en/index.php
- Grand Hotel Mercure Sophia Country Club, 4 stars:
http://www.accorhotels.com/gb/hotel-1279-grand-hotel-mercure-sophia-country-club/index.shtml
- Novotel, 4 stars:
http://www.novotel.com/gb/hotel-0398-novotel-sophia-antipolis/index.shtml